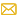
A Pneumatic Plug Valve is a type of quarter-turn valve that uses compressed air to control the flow of fluids in a piping system. It features a cylindrical or conical plug with a through-hole that can be rotated to align with the flow path (open position) or perpendicular to it (closed position). The valve is actuated by a pneumatic actuator, which provides automated and precise control. Pneumatic plug valves are widely used in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, water treatment, and food and beverage, where automation, reliability, and quick operation are essential.
Key Specifications:
- Widely used in industries such as petroleum, chemical industry, pharmacy, chemical fertilizer, power and industry
- Nominal pressure: class 150 to 900lb
- PN: 1.0 to 16.0
- Working temperature: -29 to 550°C
- Has reasonable structure, reliable sealing, excellent performance and nice appearance
- According to various conditions, 3 ways, 4 ways plug valve can be designed into multiple media flowing forms (example L type or T type) or all kinds of material (example iron, cast steel and stainless steel ) or sealing type (example metal to metal, sleeve and lubricated type)
- Materials of parts and sizes of flanges can be reasonably configured according actual operating condition of requirements of customers, so as to meet various needs of engineering
Key Features:
-
Pneumatic Actuation:
-
Operated by a pneumatic actuator, which uses compressed air to automate the valve's opening and closing.
-
Provides fast and precise control, making it ideal for applications requiring frequent operation.
-
-
Quarter-Turn Operation:
-
The plug rotates 90 degrees to open or close the valve, allowing for quick and efficient flow control.
-
Suitable for both on/off and throttling applications.
-
-
Plug Design:
-
Features a cylindrical or conical plug with a through-hole that aligns with the flow path in the open position.
-
The plug can be lubricated or non-lubricated, depending on the design and application.
-
-
Materials:
-
Constructed from durable materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, or alloys, depending on the application and fluid compatibility.
-
Sealing surfaces are often made from PTFE or elastomers for enhanced performance.
-
-
Applications:
-
Commonly used in oil and gas pipelines, chemical processing, water treatment, food and beverage, and pharmaceutical industries.
-
Suitable for handling liquids, gases, and slurries in high-pressure and high-temperature environments.
-
-
Advantages:
-
Provides reliable and automated flow control with minimal pressure drop.
-
Durable and long-lasting in harsh operating conditions.
-
Easy to integrate into automated systems.
-
Available in various sizes, pressure ratings, and configurations.
-






 Request a Quote
Request a Quote